Long covidu2014mechanisms, risk factors, and management The BMJ - famotidine chien
Long covidu2014mechanisms, risk factors, and management The BMJ
NSAID-induced injury of gastric epithelial cells is reversible
Related

Extensive Causative Esophagitis Caused by Thermal Injury: A Case

Gastric Adenocarcinoma disease: Malacards - Research Articles
Characterization of Long-Term Cultured c-kit+ Cardiac Stem Cells

Lipoic acid stimulates cAMP production via G protein-coupled

Use of gastric acidu2013suppressive agents increases the risk of
Extensive Causative Esophagitis Caused by Thermal Injury: A Case

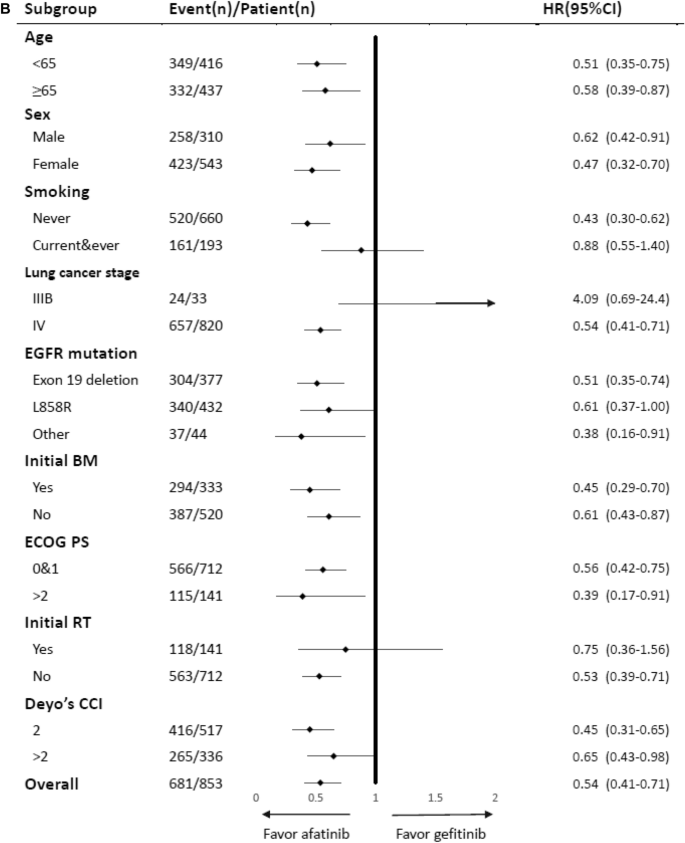
The efficacy of first-line tyrosine kinase inhibitors combined
NSAID-induced injury of gastric epithelial cells is reversible

Managing Drug Interactions in Cancer Therapy: A Guide for the

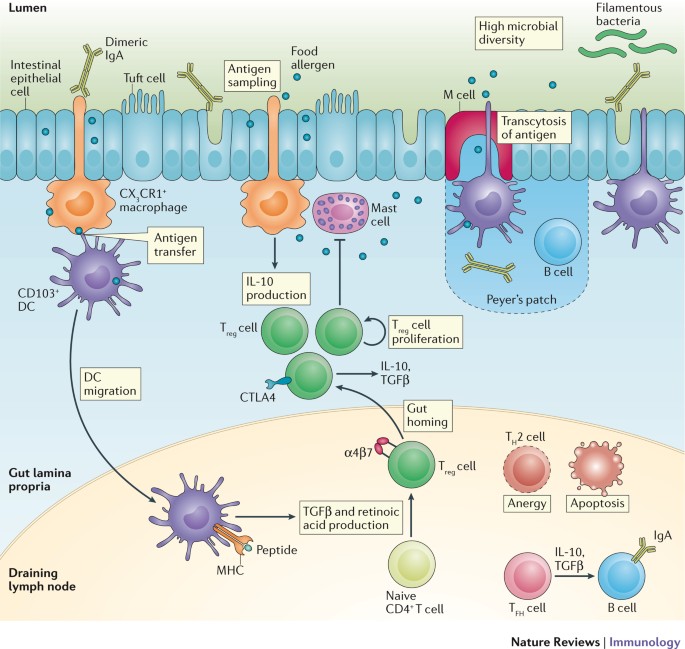
Food allergy: immune mechanisms, diagnosis and immunotherapy


0 Response to "Long covidu2014mechanisms, risk factors, and management The BMJ - famotidine chien"
Post a Comment